Content
- How is an environment analysis structered?
- What is the benefit of the environment analysis?
- What is a stakeholder?
- What is the purpose of a stakeholder analysis?
- How is the stakeholder analysis structured?
- What are the stakeholder strategies?
When starting a project, it is important to be aware of the project environment.
This is what the environmental analysis is for. It is a tool for identifying all social and factual environmental factors.
It also serves as a basis for the stakeholder analysis.
How is an environment analysis structured?
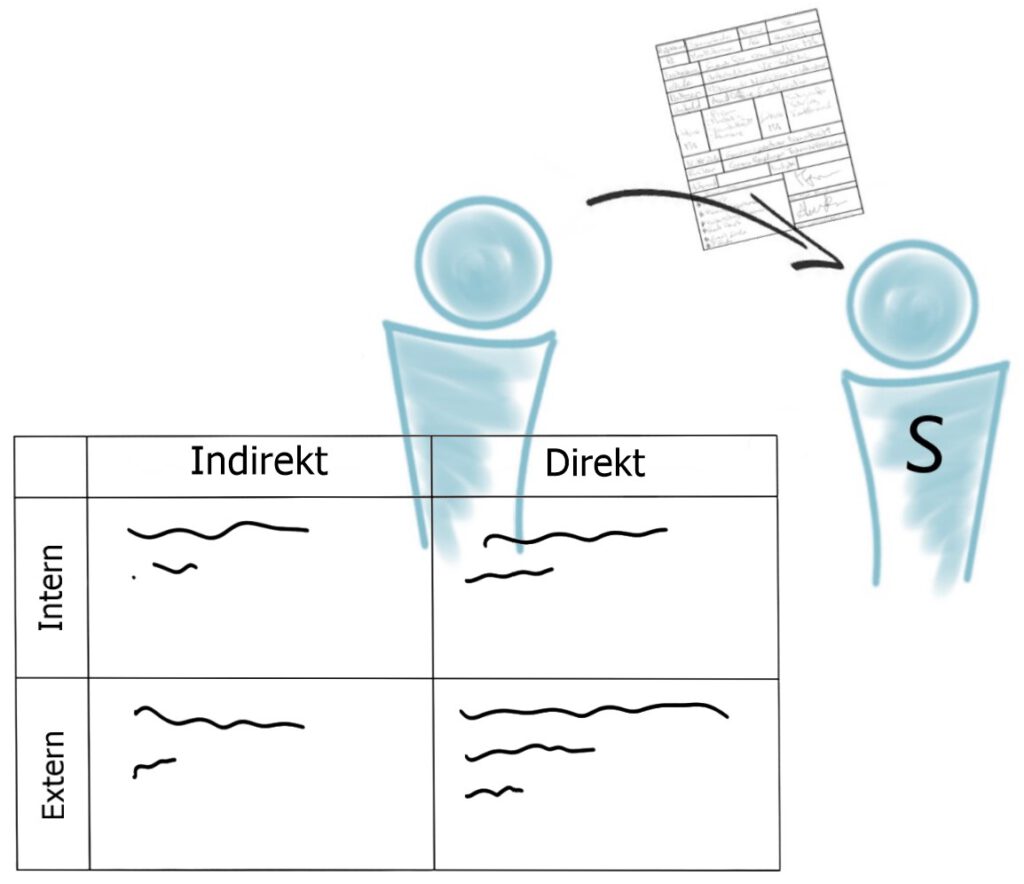
Classically, a distinction is made between 4 factors.
One between factual and social factors, and one between internal and external factors.
This is then presented in table format.
| Factual | Social | |
| Internal | Business processes and infrastructure | Internal project staff |
| External | Legal paragraphs | External project participants |
What is the benefit of the environment analysis?
In addition to stakeholder identification, it also shows necessary legal regulations and relevant company processes. This helps as a basis for further work packages:
For example, if approvals have to be obtained or certain applications have to be submitted, this can be identified from the environment analysis and this task can be tackled at an early stage.
What is a stakeholder?
In the project environment, a stakeholder has little to do with barbecues and barbeques and is not an enemy of vegetarians.
In a project, a stakeholder is defined as a person or group of people who have an interest in the (successful) progress of the project.
What is the purpose of a stakeholder analysis?
The stakeholder analysis is a tool for dealing with the individual stakeholders in the project. This clarifies their influence, setting as a basis for the respective individual management strategy.
How is the stakeholder analysis structured?
First, all stakeholders are listed. Then, for each stakeholder, their attitude towards the project, their influence on it and whether there is a potential for conflict are worked out. Then interests, expectations and fears about the project are analyzed. This information is then used to determine the handling strategy and the individual measures, as well as a responsible person. It should be noted that there can only be one person responsible for each stakeholder, and it is also important to serve each stakeholder individually according to their needs to achieve the greatest possible efficiency.
What are the stakeholder strategies?
There are four ways of dealing with stakeholders: participative, discursive, informative and repressive. As a rule, participative and informative are the most common forms.
- Participative: Involve the stakeholder in the planning process in an active way (typical for stakeholders with a positive attitude and high influence).
- Discursive: Engage in discourse with the stakeholder, evaluate, listen to concerns, resolve disagreements, reach an agreement (typical of stakeholders with negative attitudes and high influence on the project).
- Informative: Inform stakeholders in an appropriate way (typical for stakeholders with low involvement and influence).
- Repressive: share and disclose facts, do not disclose additional information, ignore stakeholders’ concerns (typical for stakeholders with negative attitudes and low influence)



0 Comments